GB: What is the difference(s) between Post-Completion point countries and Pre-Decision point countries as published on your website on September 17? At what point is a country eligible to be enlisted onto the fund’s list of Post-Completion-point countries?
IMF: Countries that have qualified for irrevocable debt relief under the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) Initiative / Multilateral Debt Relief Initiative (MDRI) framework are called post-completion point countries. Countries that are yet to start the process are called pre-decision point countries. Currently, 36 countries have reached their completion point under the HIPC/MDRI.
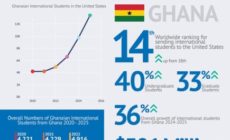
GB: When did Ghana make it onto the list of Post-Completion point countries?
IMF: Ghana reached it decision point in February 2002 and its completion point in July 2004.
GB: Under the HIPC initiative, how many times can a country benefit from the debt relief initiative from the Fund and the other multilateral institutions?
IMF: Countries are eligible to benefit from debt relief only once under the HIPC/MDRI framework.
GB: Based on the criteria for HIPC eligibility, is Ghana – in its current state – qualified for a debt relief and what would be your advice to the government with regard to that?
IMF: No, Ghana no longer qualifies for the HIPC initiative, given that it has received debt relief before.
GB: Will the fund consider advising Ghana to consider a HIPC debt relief (if the country qualifies to access HIPC for the second time), especially now that its debt-to-GDP ratio is hovering around 65/75 per cent mark?
IMF: As stated before, Ghana has already received debt relief under the HIPC initiative and can therefore not pursue further relief under this initiative.
GB: Generally, what are your comments to the Ghanaian authorities as far as HIPC and national debt stock is concerned?
Again, Ghana has already received debt relief under HIPC. With regard to national debt, based on the debt sustainability analysis prepared by IMF and World Bank staff, Ghana is now assessed to be at a high risk of debt distress. In these circumstances, reducing the debt burden and associated vulnerabilities is a priority.
The government’s ambitious and front loaded fiscal consolidation plans, which are on track, aim at bringing the public debt burden gradually down to a more sustainable level. — GB










 (Selorm) |
(Selorm) |  (Nana Kwesi)
(Nana Kwesi)