Ghana’s economy recovering faster than expected – BoG Governor
- Posted on
- Comment
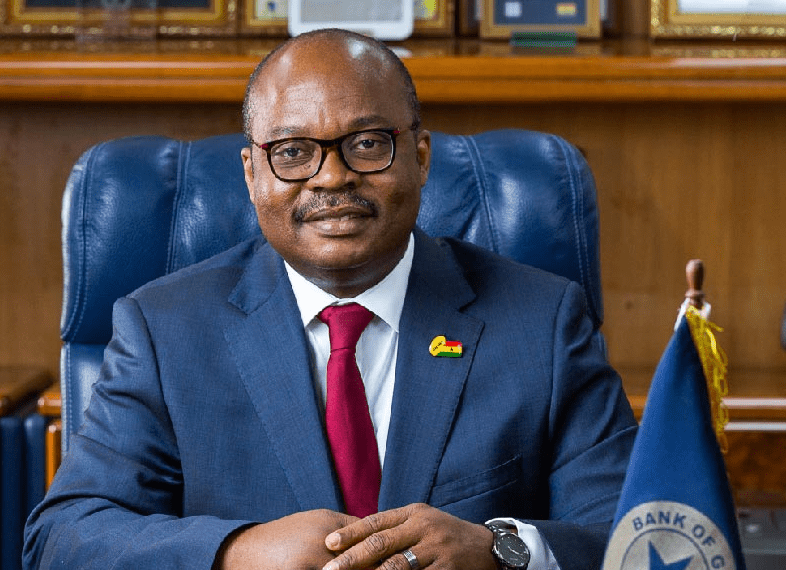
Governor of the Bank of Ghana (BoG) Dr Ernest Addison has said evidence from high frequency indicators – the CIEA outturn for October 2020, improved consumer and business confidence, and strong liquidity flows – have helped to deliver a faster than expected recovery in economic activity.
These flows, he said, include payments to contractors, Special Deposit Taking Deposit Institutions (SDI) depositors, clients of the Security and Exchange Commission (SEC) licenced fund managers, micro and small business loans provided by government through the National Board for Small Scale Industries, and the policy and regulatory reliefs to banks and SDIs.
Speaking at the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) press comferfenc in Accra on Monday, the Governor said “Based on these observations, the Bank maintains that growth will perform better than earlier projected.”
He added “The Committee noted that performance of the banking sector remains strong. The sector recorded strong growth in deposits and investments and solvency indicators were significantly higher than regulatory thresholds. Pandemic tailrisks, that is, pandemic-related impact on non-performing loans, would require continuous supervisory vigilance.
“On budget implementation, the Committee noted that the expansionary fiscal stance to address the COVID-19 pandemic has also led to deviation from the path of fiscal consolidation. Looking ahead to 2021, a decisive fiscal correction plan would be needed to contain fiscal risks in the medium-term.
“The Committee noted that inflation has eased following the spike to 11.4 percent. At 10.1 percent for October 2020, inflation is almost at the upper band target.
“The fiscal and monetary policy measures, which have increased liquidity in the economy, appear not to be impacting inflation, partly due to the existence of the output gap. As a result, the Committee expects these conditions to support inflation to return to its central path by the second quarter of 2021.
“To conclude, the Committee noted that macroeconomic conditions have generally improved relative to conditions at the time of the last MPC meeting in September 2020.
“Global conditions continue to be supportive, domestic inflation is easing, growth prospects are improving, crude oil prices have stabilized, monetary aggregates have expanded but with minimal impact on inflation, the current account deficit is stable, remittances inflow has remained firm, the exchange rate has been stable and reserve buffers continue to remain strong.
“The key risks are the evolution of the budget deficit and the financing needs to support budget implementation and the uncertainty surrounding the pandemic.
“Under the circumstances, the Committee’s decided to maintain the policy rate at 14.5 percent.”
By Laud Nartey










 (Selorm) |
(Selorm) |  (Nana Kwesi)
(Nana Kwesi)