Monkeypox Outbreak: What you need to know about it
- Posted on
- Comment

Monkeypox is a zoonotic disease caused by the Monkeypox virus and can be spread from animals to humans by coming into contact with blood, body fluids and lesions of infected animals (squirrels, rats, monkeys and others).
The Ghana Health Service (GHS) states that it could also be gotten by consuming poorly cooked meat and animal products of infected animals.
It could also be spread from human to human through droplets from coughing, sneezing, contact with blood, body fluids and rash of infected individuals, as well as contact with contaminated clothing and linens of infected individuals.
The Service explains that it could take between five to 21 days from the time of contact with an infected person or animal for one to start showing symptoms.
Symptoms of the disease include Fever (increased body temperature), headache, body ache, weakness, and swelling of lymph nodes.
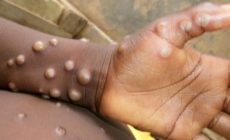
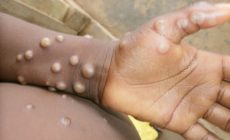
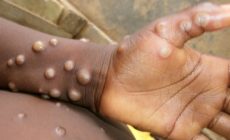
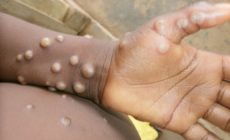
The fever is followed by the development of skin rash (within one to three days) on the entire body, however, it is more concentrated on the face and limbs.
On the characteristics of the rash, the GHS said they varied from a few to thousands from the soles of the feet, palms of the hands, mucosal membranes, conjunctiva, to cornea and could also affect the genital.
Most people, it said would recover fully from the disease (which may take up to four weeks).
It might also be mild or severe in one patient or the other and could cause death in some cases.
The GHS, therefore, entreated the public to protect themselves by avoiding contact with animals that could harbour the virus, including dead animals and avoid eating the meat of animals that could harbour the virus or ensure they were thoroughly cooked.
It also advised them to practise good personal hygiene (including hand hygiene) always, especially after contact with infected animals or humans and report immediately to the nearest health facility if they experienced any skin rash or symptoms.
-GNA






 (Selorm) |
(Selorm) |  (Nana Kwesi)
(Nana Kwesi)